In the world of boating, there are two materials that dominate the market: aluminum and fiberglass. Both have unique advantages and disadvantages that make them suitable for different types of boating activities. In this article, we will delve into the differences between aluminum and fiberglass boats to help you make an informed decision when purchasing your next vessel.
| Key Takeaways |
|---|
| Aluminum boats are generally less expensive, lighter, and easier to maintain. |
| Aluminum boats are more durable in terms of handling impacts (they dent rather than crack). |
| Aluminum boats are a good choice for activities like fishing in shallow or rocky waters. |
| Aluminum boats are less stable in choppy conditions and can be noisier at high speeds. |
| Fiberglass boats are typically more expensive and heavier. |
| Fiberglass boats offer more stability in choppy conditions and are quieter at high speeds. |
| Fiberglass boats are more aesthetically pleasing and easier to customize. |
| Fiberglass boats are better suited for water sports and open water cruising. |
| Fiberglass boats require more maintenance and have higher repair costs. |
| The choice between aluminum and fiberglass boats depends on specific needs and preferences. |

Definition of Aluminum and Fiberglass boats
Aluminum boats are made entirely or partially of aluminum, a lightweight and durable metal that is resistant to corrosion. These boats can range from small fishing boats to large commercial vessels due to their versatility in design and construction.
On the other hand, fiberglass boats are constructed using composite materials such as resin and glass fiber. They are known for their sleek appearance, heavier but more stable nature, and resistance to water damage.
Brief History of the Two Materials in Boat Building
The use of aluminum in boat building dates back to World War II when it was used as a substitute for steel due to its lightness and corrosion-resistant properties. Since then, it has gained popularity among manufacturers because it allows for greater customization in design while maintaining strength.
Fiberglass boat construction began in the 1940s when a chemist named John Koster created an innovative process using resin and glass fibers to create a strong yet lightweight material for boat hulls. This new material quickly caught on with manufacturers due to its durability, ease of production, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional wooden boats.
Comparison
| Application/Feature/Trait | Aluminum Hull | Fiberglass Hull |
|---|---|---|
| Price | Less expensive | More expensive |
| Weight | Lighter, easier to handle and launch | Heavier, more stable in water |
| Handling in heavy waves | Less stable in choppy conditions | More stable due to higher weight |
| Fuel efficiency | More fuel efficient due to lighter weight | Less fuel efficient due to heavier weight |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance, no need to wax | Higher maintenance, requires waxing |
| Durability | More durable, dents instead of cracking | Less durable, can crack or break |
| Repair cost | Lower repair cost, dents can be easily fixed | Higher repair cost, cracks require special equipment to fix |
| Customization | Difficult to customize due to less malleability | Easier to customize due to malleability of fiberglass |
| Noise | Noisier, especially at high speeds | Quieter, even at high speeds |
| Corrosion | Subject to corrosion | Less prone to corrosion |
| Aesthetics | Less sleek, more utilitarian | Sleeker, more aesthetically pleasing |
| Safety | Strong when impacting hard objects, but more susceptible to being knocked around by waves or high winds | More prone to being punctured or cracked by hard objects, but a more stable ride in rough conditions |
| Environmental Impact | More environmentally friendly, easier to recycle | Less environmentally friendly, difficult to recycle |
| Resale Value | Lower resale value due to reputation of being cheaply made | Excellent within the first 8 years, good between 9-15 years, and it starts to decrease after that |
| Fishing in shallow water | Better suited due to lighter weight and durability | Not recommended due to the hull being damaged by contacting rocks and gravel |
| Handling in windy conditions | Drifts faster due to lighter weight | Drifts slower due to heavier weight |
| Towing and hauling | Cheaper to transport because of the lighter weight, but also more difficult to back the boat up at the launch due to the lighter weight (tends to be more sensitive) | More expensive to tow because of how heavy it is, but easier to back the boat up at the launch because it is less sensitive to small changes of the steering wheel |
| Water sports (e.g., water skiing) | Less suitable | More suitable due to stability and weight |
| Comfort | Less comfortable, less smooth ride | More comfortable, smoother ride |
| Longevity | Longer lifespan due to toughness and durability | 20-25 years before the gel coat and hull start to really be impacted by UV light, prone to spider-cracks at any time |
| Geographical Considerations | Better for rocky shorelines and easy launching | Better for open waters and comfortable cruising |
The purpose of comparing aluminum vs. fiberglass boats is not only important for buyers but also manufacturers who want to understand which material is best suited for specific types of vessels or activities.
By examining the strengths and weaknesses of each material as well as their performance capabilities, we can determine which material is better for certain types of boating activities such as fishing, leisure cruising, or water sports. Additionally, considering the cost of each material is also important as it can greatly affect the overall affordability and accessibility of boating.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Aluminum Boats
Durability and Strengths
Aluminum boats are known for their durability and strength, which makes them popular with fishermen, hunters, and other boaters who need a vessel that can withstand harsh environments (think of stumps, rocks, and gravel). Also, one of the biggest advantages of aluminum boats is their resistance to corrosion.
This is because aluminum has a protective oxide layer that forms on its surface when it’s exposed to air. This layer prevents further corrosion from occurring, which means that aluminum boats can last for decades without showing signs of wear and tear.
Denting might be seen as a weakness, but it’s actually a strength of aluminum hulls based on the the application. Aluminum boats are far superior to fiberglass at handling water that contains stumps, rocks, and other hard objects. Instead of cracking, like fiberglass, aluminum just absorbs the blow and a dent is formed. This trait allows these boats to be used and abused for fisherman and sportsman alike.
Another strength of aluminum boats is their high tensile strength. Tensile strength refers to a material’s ability to resist breaking under tension or stress.
Aluminum has a high tensile strength compared to other materials used in boat building, including fiberglass. This means that an aluminum boat can withstand heavy loads without bending or cracking.
Aluminum boat hulls generally are around 0.125″ or about 3-4mm in thickness.
Aluminum boats are known for their longevity. Because they don’t corrode as easily as other materials, they tend to last longer than fiberglass or wood boats.
Weaknesses
Despite all their strengths, aluminum boats do have some weaknesses that should be considered before purchasing one. One weakness is their susceptibility to dents (also a strength, if you consider that denting is better than cracking). Although aluminum is strong and durable, it’s also malleable, which means that it can dent easily if it’s hit hard enough.
Another weakness of aluminum boats is their tendency to oxidize over time. Oxidation occurs when the protective oxide layer on the surface of the metal breaks down due to exposure to moisture or other environmental factors.
This can cause the boat’s appearance to deteriorate over time if it’s not properly maintained. Aluminum boats have poor thermal insulation compared to other materials such as fiberglass or wood.
This means that they’re more susceptible to temperature changes in the water and air around them than other types of boats. This can lead to uncomfortable conditions for passengers in extreme temperatures.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Fiberglass Boats
Durability and Strengths
Fiberglass boats are known for their durability, strength, and resilience. They are made of a composite material that is reinforced with fibers of glass.
This makes them resistant to impact, abrasion, and puncture damage. Fiberglass boats also have a higher weight capacity than aluminum boats, allowing for more gear and additional passengers to be carried.
Heavier
One of the biggest advantages of fiberglass boats is their heavier construction. Fiberglass hulls are much heavier than aluminum, which makes fiberglass boats more stable in the water and less susceptible to erratic drifting with wind and waves. This does come with the cost of requiring more power and fuel to push the boat through the water, but the smoother ride can definitely be worth it.
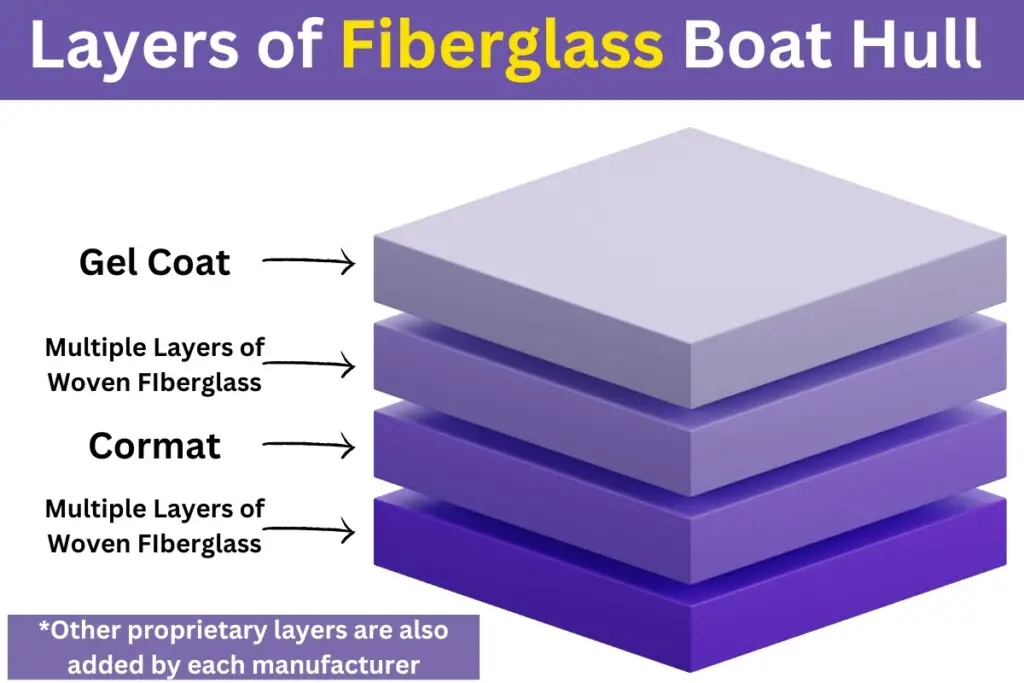
The reason for fiberglass hulls being so heavy is the shear number of layers that go into creating it. When all is said and done, it’s not uncommon for the hull to be about 5/16″ – 3/8″ thick, or about 8-10mm. This is about 3x the thickness of aluminum hulls.
Working from the outside inward, the layers generally include (depending on the manufacturer which could add more proprietary materials) the following:
- Wax
- Exterior Gel Coat
- Multiple layers of alternating woven fiberglass
- Cormat (a foam core)
- Multiple layers of alternating woven fiberglass
Smooth Ride and Low Maintenance Cost
Fiberglass is an excellent material for creating smooth hulls that glide effortlessly through the water. The flexibility and weight of fiberglass allows it to absorb shocks from rough waters (not collision with hard objects) better than other materials like aluminum or wood.
Fiberglass is also relatively easy to maintain compared to other materials used in boat building such as wood or steel. They require little maintenance apart from regular cleaning with soap and water, and waxing once or twice per year.
Weaknesses
Although fiberglass boats are strong and durable, they do have some weaknesses worth noting. One critical issue with fiberglass is its poor resistance to UV light; over time it causes discoloration or fading on the surface of the boat which then may affect its resale value or overall aesthetic appeal.
Another downfall of fiberglass hulls is that when struck by something hard, they don’t dent like aluminum, the layers begin to crack.
Spider cracks are notorious with fiberglass hulls and decks. These are the super thin cracks that start at one location and expand out in a pattern that resembles a spider web. You can check out my article here on how to address these cracks.
Cracks can be difficult to repair if found after initial construction; this can pose challenges when trying to sell a used vessel because it will require costly repairs before resale. Although fiberglass has impressive strength compared to its weight ratio during initial use (which results in a long lifespan), it breaks down over time due to UV exposure or ice and water damage.
Unlike aluminum boats, fiberglass boats have a limited lifespan. The average lifespan of a fiberglass boat is about 20-30 years before it needs extensive repairs or replacement.
Performance Comparison between Aluminum and Fiberglass Boats
Speed and Maneuverability
When it comes to maneuverability, fiberglass boats tend to excel. The heavy, smooth, and aerodynamic hull of a fiberglass boat allows it to glide through the water with minimal resistance and with minimal impact from waves and winds.
On the other hand, aluminum boats are lighter and are much faster in the water, but are more prone to drifting and rougher rides with choppy waves.
However, because of their heavier weight and better handling in the water, fiberglass boats tend to be more enjoyable than aluminum boats for activities like water skiing or wakeboarding where quick but stable turns are necessary.
Fuel Efficiency
Fuel efficiency is an important consideration when choosing a boat. In general, aluminum boats tend to be more fuel-efficient than fiberglass boats. This is due in large part to their lighter weight and the fact that aluminum boats do not need as large of an engine to accomplish the same speeds.
Also, since aluminum boats are lighter weight, they are cheaper to tow since your truck will be burning less fuel. This saves you money not only on the way to the lake, but when on the lake as well due to the smaller engine requirement.
Comfort Level
Comfort is another important factor when choosing a boat. Both aluminum and fiberglass boats offer certain advantages in terms of comfort. Fiberglass boats tend to be quieter on the water as they do not transmit vibrations from waves or engine noise as strongly as aluminum boats do.
They also absorb the impact of waves and wind better which results in less jarring while underway. Many aluminum boats offer excellent stability as well thanks to their wide beam (the width of the boat) which in many models are comparable to fiberglass.
Fiberglass have a distinct advantage in that they can generally be outfitted with far more accessories and “stations” on your vessel, due to the ease of making fiberglass into any shape, whereas aluminum boats tend to fall short. On fiberglass boats you’ll find livewells, tackle stations, fishboxes, cabins, and other modules integrated right into the design of the boat.
Cost Comparison between Aluminum and Fiberglass Boats
The cost of purchasing a boat is one of the most important factors that buyers consider. When comparing aluminum and fiberglass boats, it is essential to analyze the initial costs.
Almost without exception, fiberglass boats are more expensive than fiberglass boats of similar sizes and designs. However, this might not always be the case as some high-end aluminum models can be more expensive than fiberglass boats.
In fact, when I looked up 15 boat manufacturers and compared 124 boat models (fiberglass and aluminum), I found that fiberglass boats are nearly 100% more expensive than aluminum boats per foot of length.
| Boat Hull Material | Average Cost Per Foot of Length |
|---|---|
| Fiberglass | $3,659 |
| Aluminum | $1,832 |
The price difference between the two materials mostly depends on the manufacturer, size, and quality level. When it comes to maintenance costs, aluminum boats tend to be less expensive compared to fiberglass ones.
They require less maintenance due to their resistant nature against corrosion and abrasion. Aluminum vessels do not require frequent cleaning or repainting like their fiberglass counterparts.
Aluminum boats are cheaper to tow since they require less fuel from your vehicle to pull them, and they are also cheaper to drive on the water since they do not require as large of an engine to enjoy the same speeds.
Final Takeaways
Whether to choose an aluminum or a fiberglass boat depends on various factors such as intended use, budgetary constraints, location of use, and personal preferences among others. Both materials have their strengths and weaknesses that can affect performance and cost in different ways.
If you’re looking for a utilitarian boat that you will use and abuse, go with aluminum. Hunters and fisherman are prime candidates for aluminum.
If you’re looking for a smooth ride, an aesthetically pleasing boat, and more maintenance to keep it looking that way — then go fiberglass. People who are out just to enjoy the boating experience (eating, socializing, water sports) will be prime candidates for fiberglass.
Aluminum boats generally have lower initial prices and lower maintenance costs in the long run due to their durability and resistance to corrosion. On the other hand, fiberglass vessels tend to have higher upfront costs and require more maintenance over time due to susceptibility to damage from UV light exposure and cracking in the hull’s gel coat.
Ultimately, buying a boat is an investment that requires careful consideration of all relevant factors before making a final decision. By understanding the key differences in cost between aluminum versus fiberglass boats presented above, buyers can make informed choices when purchasing either type of vessel based on their unique needs and preferences.